Ciprofloxacin is a widely used antibiotic belonging to the fluoroquinolone class. It is known for its broad-spectrum activity against a variety of bacterial infections, making it a versatile and effective treatment option. Ciprofloxacin is commonly prescribed for infections of the urinary tract, respiratory system, skin, bones, and gastrointestinal tract, among others. Despite its effectiveness, ciprofloxacin is not without risks, and understanding its uses, benefits, side effects, dosage, and warnings is essential for safe and effective use.
This comprehensive article explores ciprofloxacin in detail, covering its mechanism of action, medical uses, benefits, potential side effects, recommended dosages, and important precautions. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of ciprofloxacin and how to use it responsibly.
What is Ciprofloxacin?
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic that works by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes essential for DNA replication, transcription, and repair. By targeting these enzymes, ciprofloxacin effectively kills bacteria or prevents their growth. It is available in various forms, including oral tablets, extended-release tablets, oral suspensions, and intravenous (IV) formulations. Ciprofloxacin is sold under several brand names, including Cipro, Cipro XR, and Proquin XR.
Ciprofloxacin is commonly used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including those caused by Gram-negative and some Gram-positive bacteria. Its broad-spectrum activity and availability in multiple formulations make it a popular choice for both outpatient and inpatient treatment.
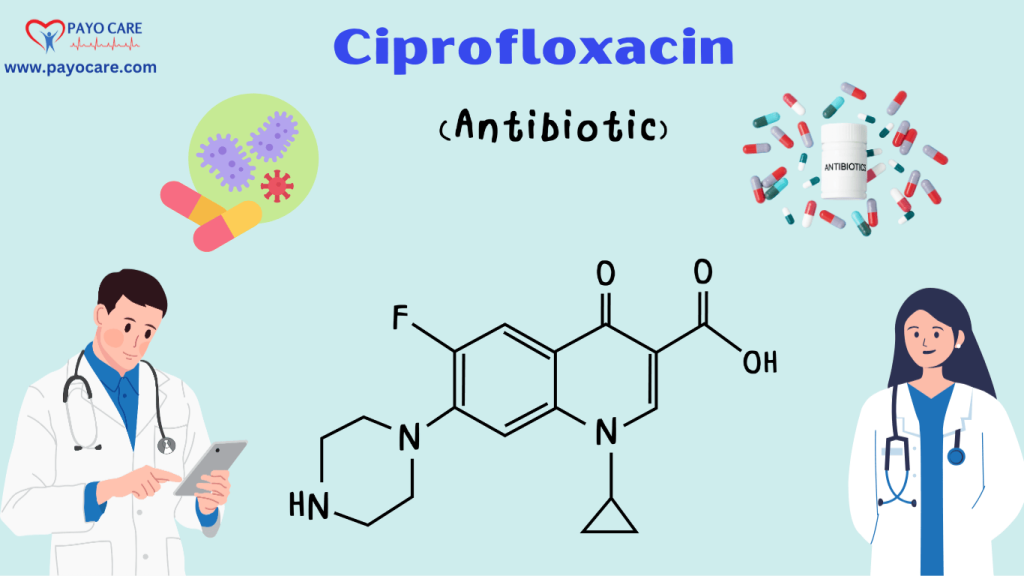
Mechanism of Action
Ciprofloxacin works by targeting bacterial enzymes involved in DNA replication and repair:
- Inhibition of DNA Gyrase: Ciprofloxacin inhibits DNA gyrase, an enzyme that introduces negative supercoils into DNA, allowing it to unwind and replicate.
- Inhibition of Topoisomerase IV: Ciprofloxacin also inhibits topoisomerase IV, an enzyme that separates replicated DNA strands during cell division.
By inhibiting these enzymes, ciprofloxacin disrupts bacterial DNA replication and repair, leading to bacterial cell death. This mechanism of action makes ciprofloxacin effective against a wide range of bacteria, including both Gram-negative and Gram-positive organisms.
Medical Uses of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including:
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Ciprofloxacin is commonly prescribed for:
- Uncomplicated and complicated UTIs
- Pyelonephritis (kidney infections)
2. Respiratory Tract Infections
Ciprofloxacin is effective for:
- Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis
- Community-acquired pneumonia (in certain cases)
3. Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Ciprofloxacin is used to treat:
- Cellulitis
- Wound infections
- Abscesses
4. Bone and Joint Infections
Ciprofloxacin is prescribed for:
- Osteomyelitis (bone infections)
- Septic arthritis
5. Gastrointestinal Infections
Ciprofloxacin is effective against:
- Traveler’s diarrhea
- Typhoid fever
- Bacterial gastroenteritis
6. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Ciprofloxacin is used to treat:
- Gonorrhea (in certain cases)
7. Prophylaxis
Ciprofloxacin is used to prevent infections in:
- Patients undergoing surgery
- Individuals exposed to anthrax
Benefits of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin offers several benefits, making it a valuable antibiotic for treating bacterial infections. Below are some of the key benefits:
1. Broad-Spectrum Activity
Ciprofloxacin is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including both Gram-negative and Gram-positive organisms.
2. Versatile Formulations
Ciprofloxacin is available in oral, IV, and extended-release formulations, allowing for tailored treatment based on the infection and patient needs.
3. Rapid Onset of Action
Ciprofloxacin provides relatively fast relief from bacterial infections, making it suitable for acute and severe infections.
4. Effective for Resistant Infections
Ciprofloxacin is often effective against bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics, making it a valuable option for complicated infections.
5. Prophylactic Use
Ciprofloxacin is effective in preventing infections in high-risk individuals, such as those undergoing surgery or exposed to anthrax.
Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
While ciprofloxacin is generally safe when used as directed, it can cause side effects, particularly with long-term use or high doses. Some of the most common side effects include:
1. Gastrointestinal Issues
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
2. Central Nervous System Effects
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Insomnia
- Nervousness
3. Musculoskeletal Effects
- Tendonitis
- Tendon rupture (rare but serious)
- Muscle pain
4. Allergic Reactions
- Rash
- Hives
- Swelling
- Difficulty breathing
5. Cardiovascular Effects
- QT prolongation (rare but serious)
- Arrhythmias
6. Hepatotoxicity
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Jaundice
7. Photosensitivity
- Increased sensitivity to sunlight, leading to sunburn or rash
8. Clostridioides difficile Infection
- Risk of developing C. difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) due to disruption of normal gut flora
Dosage Recommendations
The appropriate dosage of ciprofloxacin depends on the type and severity of the infection, the formulation used, and the individual’s medical history. Below are general guidelines for ciprofloxacin dosage:
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Uncomplicated UTIs: 250–500 mg twice daily for 3–7 days.
- Complicated UTIs: 500–750 mg twice daily for 7–14 days.
2. Respiratory Tract Infections
- Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis: 500 mg twice daily for 7–14 days.
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia: 500–750 mg twice daily for 7–14 days.
3. Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Mild to Moderate Infections: 500 mg twice daily for 7–14 days.
- Severe Infections: 750 mg twice daily for 7–14 days.
4. Bone and Joint Infections
- Osteomyelitis: 500–750 mg twice daily for 4–6 weeks or longer.
- Septic Arthritis: 500–750 mg twice daily for 4–6 weeks.
5. Gastrointestinal Infections
- Traveler’s Diarrhea: 500 mg twice daily for 1–3 days.
- Typhoid Fever: 500 mg twice daily for 10 days.
6. Intravenous (IV) Ciprofloxacin
- Severe Infections: 400 mg every 8–12 hours, depending on the infection.
It is important to follow the dosage instructions provided by a healthcare professional and to complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve.
Warnings and Precautions
Ciprofloxacin is a powerful antibiotic, but it is not suitable for everyone. Certain individuals should use ciprofloxacin with caution or avoid it altogether. Below are some important warnings and precautions:
1. Allergies
Individuals with a known allergy to ciprofloxacin or other fluoroquinolones should avoid using ciprofloxacin.
2. Tendon Disorders
Ciprofloxacin may increase the risk of tendonitis and tendon rupture, particularly in older adults, those taking corticosteroids, and individuals with a history of tendon disorders.
3. Central Nervous System Effects
Ciprofloxacin may cause central nervous system effects, such as dizziness, confusion, and seizures. It should be used with caution in individuals with a history of seizures or other neurological conditions.
4. QT Prolongation
Ciprofloxacin may prolong the QT interval, increasing the risk of arrhythmias. It should be used with caution in individuals with a history of heart disease or those taking other QT-prolonging medications.
5. Photosensitivity
Ciprofloxacin can increase sensitivity to sunlight, so patients should avoid excessive sun exposure and use sunscreen while taking this medication.
6. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Ciprofloxacin should be avoided during pregnancy, as it may harm the developing fetus. It is also not recommended for breastfeeding mothers.
7. Drug Interactions
Ciprofloxacin can interact with other medications, including:
- Antacids containing magnesium or aluminum
- Iron supplements
- Warfarin
- Theophylline
- Corticosteroids
Always inform your healthcare provider of all medications you are taking before starting ciprofloxacin.
Conclusion
Ciprofloxacin is a versatile and effective antibiotic for treating a wide range of bacterial infections. Its broad-spectrum activity, rapid onset of action, and availability in multiple formulations make it a valuable tool in the fight against bacterial infections. However, like all medications, ciprofloxacin is not without risks. Understanding its uses, benefits, side effects, dosage, and warnings is essential for safe and effective use.
While ciprofloxacin is widely available, it is important to consult a healthcare provider before using it, especially for long-term or high-dose treatment. By following medical advice and using ciprofloxacin responsibly, individuals can maximize its benefits while minimizing the risks.
Ciprofloxacin remains an important antibiotic in the management of bacterial infections, and its continued use underscores the importance of ongoing research and education about this medication. Whether used for acute or chronic infections, ciprofloxacin has earned its place as a trusted and effective treatment option.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is ciprofloxacin used for?
Ciprofloxacin is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections (UTIs), respiratory infections, skin infections, gastrointestinal infections, and bone/joint infections.
2. How long does it take for ciprofloxacin to work?
Ciprofloxacin starts working within a few hours, but noticeable improvement usually occurs within 1-3 days, depending on the severity of the infection.
3. Can I take ciprofloxacin on an empty stomach?
Yes, ciprofloxacin can be taken with or without food, but avoid dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt) as they can reduce its effectiveness.
4. What are the common side effects of ciprofloxacin?
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, and stomach pain.
5. Why is ciprofloxacin not recommended for everyone?
Ciprofloxacin can cause serious side effects like tendon rupture, nerve damage (neuropathy), and mental health effects. It should not be used by children, pregnant women, or people with a history of tendon disorders.
6. Can I drink alcohol while taking ciprofloxacin?
It is not recommended to drink alcohol while taking ciprofloxacin, as it may increase dizziness and drowsiness.
7. Does ciprofloxacin interact with other medications?
Yes, ciprofloxacin interacts with antacids, blood thinners (warfarin), NSAIDs, and some diabetes medications. Always inform your doctor about any medications you are taking.
8. How long should I take ciprofloxacin?
Always take the full course as prescribed, usually 3-14 days, depending on the infection. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance.
9. Can ciprofloxacin cause tendon damage?
Yes, ciprofloxacin may cause tendon pain, inflammation, or rupture, especially in older adults, athletes, and those on corticosteroids.
10. What should I do if I miss a dose of ciprofloxacin?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it is close to the time for your next dose. Do not double up to make up for a missed dose.