Ceftriaxone is a broad-spectrum antibiotic belonging to the cephalosporin class, specifically a third-generation cephalosporin. It is widely used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and serious infections such as meningitis and sepsis. Ceftriaxone is known for its effectiveness against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, making it a versatile and essential tool in modern medicine. This comprehensive guide explores the uses, benefits, side effects, dosage, warnings, and other important information about ceftriaxone.
What is Ceftriaxone?
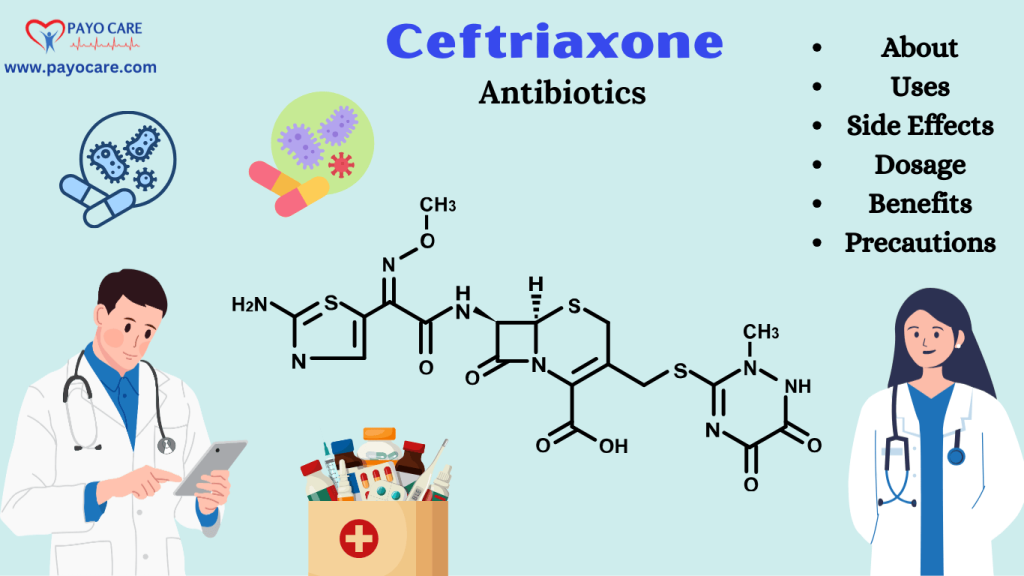
Ceftriaxone is a bactericidal antibiotic, meaning it kills bacteria by interfering with their cell wall synthesis. It is administered intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM) and is particularly effective against a wide range of bacteria, including:
- Gram-positive bacteria: Such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-sensitive strains).
- Gram-negative bacteria: Such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Haemophilus influenzae.
Ceftriaxone is often used in hospital settings due to its broad spectrum of activity and ability to penetrate various tissues and body fluids, including the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), making it effective for treating meningitis.
Uses of Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone is prescribed to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including:
1. Respiratory Tract Infections
- Pneumonia: Ceftriaxone is effective against community-acquired pneumonia caused by susceptible bacteria.
- Bronchitis: It may be used to treat acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis.
2. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Ceftriaxone is used to treat complicated UTIs, including pyelonephritis (kidney infection), caused by susceptible Gram-negative bacteria.
3. Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Ceftriaxone is effective in treating cellulitis, abscesses, and wound infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
4. Bone and Joint Infections
It is used to treat osteomyelitis (bone infection) and septic arthritis caused by susceptible organisms.
5. Intra-Abdominal Infections
Ceftriaxone is used to treat peritonitis and other intra-abdominal infections, often in combination with other antibiotics.
6. Meningitis
Ceftriaxone is a first-line treatment for bacterial meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae.
7. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
- Gonorrhea: Ceftriaxone is the preferred treatment for uncomplicated gonorrhea, often administered as a single dose.
- Syphilis: It may be used as an alternative to penicillin for treating syphilis in certain cases.
8. Sepsis
Ceftriaxone is used to treat sepsis and bacteremia (bacterial infection in the blood) caused by susceptible organisms.
9. Lyme Disease
In some cases, ceftriaxone is used to treat Lyme disease, particularly when the infection involves the central nervous system.
10. Surgical Prophylaxis
Ceftriaxone may be used to prevent infections in patients undergoing certain types of surgery.
Benefits of Ceftriaxone
1. Broad-Spectrum Activity
Ceftriaxone is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, making it a versatile antibiotic for treating various infections.
2. High Tissue Penetration
Ceftriaxone penetrates well into tissues and body fluids, including the cerebrospinal fluid, making it effective for treating serious infections like meningitis.
3. Convenient Dosing
Ceftriaxone has a long half-life, allowing for once-daily dosing in most cases, which is convenient for both patients and healthcare providers.
4. Effective Against Resistant Bacteria
Ceftriaxone is often effective against bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics, such as penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae.
5. Rapid Onset of Action
Ceftriaxone begins to work quickly, making it suitable for treating severe infections that require immediate intervention.
Side Effects of Ceftriaxone
While ceftriaxone is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some patients. These side effects can range from mild to severe and may include:
1. Common Side Effects
- Injection Site Reactions: Pain, swelling, or redness at the injection site.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain.
- Headache: Mild to moderate headaches may occur.
- Rash: Skin rash or itching.
2. Less Common Side Effects
- Elevated Liver Enzymes: Ceftriaxone may cause transient increases in liver enzymes.
- Leukopenia or Thrombocytopenia: Decreased white blood cell or platelet counts.
- Allergic Reactions: Mild allergic reactions, such as hives or itching.
3. Serious Side Effects
While rare, ceftriaxone can cause serious side effects that require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Severe Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis, characterized by difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, and rapid heartbeat.
- Clostridioides difficile Infection: Ceftriaxone can disrupt the normal gut flora, leading to C. difficile-associated diarrhea or colitis.
- Hemolytic Anemia: Ceftriaxone can cause the destruction of red blood cells, leading to anemia.
- Gallbladder Sludge or Pseudolithiasis: Ceftriaxone can cause reversible gallbladder sludge or pseudolithiasis, particularly in children.
- Kidney Dysfunction: Ceftriaxone may cause kidney problems, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney disease.
Dosage and Administration
1. Recommended Dosage
The dosage of ceftriaxone varies depending on the type and severity of the infection, the patient’s age, and kidney function. Typical dosages include:
- Adults: 1-2 grams once daily (or every 12 hours for severe infections).
- Children: 50-100 mg/kg/day, divided into one or two doses.
- Neonates: 20-50 mg/kg/day.
2. How Ceftriaxone is Administered
- Intravenous (IV): Ceftriaxone is often administered as an IV infusion over 30 minutes.
- Intramuscular (IM): Ceftriaxone can also be given as an IM injection, often mixed with lidocaine to reduce pain.
3. Duration of Treatment
The duration of treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection. For example:
- Uncomplicated Gonorrhea: Single dose of 250 mg IM.
- Meningitis: 7-14 days of treatment.
- Bone and Joint Infections: 4-6 weeks of treatment.
4. Missed Dose
If a dose is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, the missed dose should be skipped, and the regular dosing schedule should be resumed.
5. Overdose
In case of an overdose, seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms of overdose may include seizures, severe gastrointestinal upset, or kidney dysfunction.

Warnings and Precautions
1. Allergic Reactions
Patients with a history of allergic reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins, or other beta-lactam antibiotics should use ceftriaxone with caution. Cross-reactivity between penicillins and cephalosporins is possible.
2. Clostridioides difficile Infection
Ceftriaxone can disrupt the normal gut flora, increasing the risk of C. difficile-associated diarrhea or colitis. Patients should be monitored for symptoms such as persistent diarrhea, abdominal pain, or fever.
3. Gallbladder Sludge or Pseudolithiasis
Ceftriaxone can cause reversible gallbladder sludge or pseudolithiasis, particularly in children. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting.
4. Hemolytic Anemia
Ceftriaxone can cause hemolytic anemia, especially in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. Patients should be monitored for signs of anemia, such as fatigue, pale skin, or shortness of breath.
5. Kidney and Liver Function
Ceftriaxone should be used with caution in patients with impaired kidney or liver function. Dosage adjustments may be necessary.
6. Drug Interactions
Ceftriaxone can interact with other medications, including:
- Calcium-Containing Products: Ceftriaxone should not be mixed with calcium-containing solutions, as it can lead to the formation of precipitates in the lungs or kidneys.
- Warfarin: Ceftriaxone may increase the risk of bleeding in patients taking warfarin.
- Probenecid: Probenecid can increase the levels of ceftriaxone in the blood, potentially increasing the risk of side effects.
7. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Pregnancy: Ceftriaxone is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but it should be used only if clearly needed.
- Breastfeeding: Ceftriaxone is excreted in breast milk in small amounts. Consult your healthcare provider before using ceftriaxone while breastfeeding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is ceftriaxone used for?
Ceftriaxone is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including pneumonia, meningitis, urinary tract infections, skin infections, bone and joint infections, and sepsis. It is also used for surgical prophylaxis and gonorrhea treatment.
2. How does ceftriaxone work?
Ceftriaxone works by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, which leads to the destruction of the bacteria. It is effective against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
3. What are the common side effects of ceftriaxone?
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rash, and pain or swelling at the injection site. Serious side effects may include allergic reactions, severe diarrhea (C. difficile infection), and blood disorders.
4. What is the typical dosage of ceftriaxone?
Dosage depends on the type and severity of the infection. For most infections, the usual adult dose is 1-2 grams once daily, administered intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM). Pediatric dosing is based on weight. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
5. Can ceftriaxone cause allergic reactions?
Yes, ceftriaxone can cause allergic reactions, including rash, itching, swelling, and anaphylaxis. Inform your doctor if you have a history of allergies to cephalosporins, penicillins, or other antibiotics.
6. Is ceftriaxone safe for children?
Ceftriaxone is generally safe for children when prescribed by a doctor. However, it should not be used in neonates with hyperbilirubinemia (high bilirubin levels) due to the risk of kernicterus.
7. Can ceftriaxone be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
Ceftriaxone is generally considered safe during pregnancy if prescribed by a doctor. It is also considered safe for breastfeeding mothers, as only small amounts pass into breast milk. However, consult your doctor before use.
8. What are the warnings associated with ceftriaxone?
Ceftriaxone should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal diseases (especially colitis), kidney or liver impairment, or allergies to antibiotics. It may also interact with calcium-containing products, leading to potentially fatal reactions.
9. Can ceftriaxone interact with other medications?
Yes, ceftriaxone can interact with other medications, including blood thinners (e.g., warfarin) and live vaccines. Inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you are taking.
10. How should ceftriaxone be stored?
Ceftriaxone is typically stored in a hospital or clinical setting. If administered at home, follow the storage instructions provided by your healthcare provider. It is usually stored at room temperature and protected from light.
Conclusion
Ceftriaxone is a powerful and versatile antibiotic that plays a critical role in treating a wide range of bacterial infections. Its broad-spectrum activity, high tissue penetration, and convenient dosing make it a valuable tool in both hospital and outpatient settings. However, like all medications, ceftriaxone carries risks, including allergic reactions, C. difficile infection, and potential interactions with other drugs. Patients should use ceftriaxone under the guidance of a healthcare provider and report any unusual symptoms or side effects promptly.
If you have been prescribed ceftriaxone, follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and complete the full course of treatment to ensure the infection is fully eradicated. By understanding the uses, benefits, side effects, dosage, and warnings associated with ceftriaxone, you can make informed decisions about your treatment and achieve better health outcomes.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only

