Amlodipine is a widely prescribed medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as calcium channel blockers (CCBs). It is primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and certain types of chest pain (angina). Amlodipine is known for its effectiveness in managing these conditions, and it is often prescribed as a first-line treatment due to its safety profile and ease of use. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the uses, benefits, side effects, dosage, warnings, and other important information about Amlodipine.
What is Amlodipine?
Amlodipine is a medication that works by relaxing the blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily. This helps to lower blood pressure and reduce the workload on the heart. It is available in both brand-name and generic forms and is commonly prescribed under the brand name Norvasc.
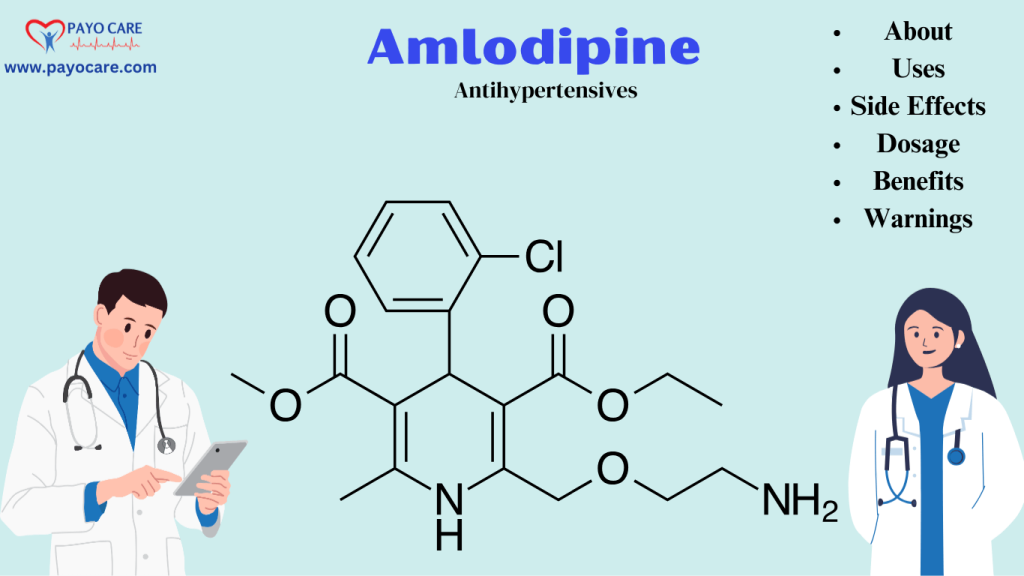
Amlodipine is classified as a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It specifically blocks the influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle, which leads to the relaxation of blood vessels and a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance. This mechanism of action makes Amlodipine effective in treating hypertension and angina.
Uses of Amlodipine
1. Treatment of Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Hypertension is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. If left untreated, it can lead to serious health complications such as heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. Amlodipine is often prescribed to help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of these complications.
By relaxing the blood vessels, Amlodipine allows blood to flow more freely, which helps to lower blood pressure. It is often used as a first-line treatment for hypertension, either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive medications.
2. Management of Chronic Stable Angina
Angina is a type of chest pain that occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. Chronic stable angina is characterized by predictable chest pain that occurs during physical exertion or stress. Amlodipine is used to manage this condition by improving blood flow to the heart muscle and reducing the frequency and severity of angina episodes.
3. Vasospastic Angina (Prinzmetal’s or Variant Angina)
Vasospastic angina, also known as Prinzmetal’s or variant angina, is a type of angina that occurs due to spasms in the coronary arteries. Amlodipine is effective in preventing these spasms and reducing the occurrence of chest pain associated with this condition.
4. Off-Label Uses
In addition to its approved uses, Amlodipine is sometimes prescribed off-label for other conditions, such as:
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon: A condition characterized by reduced blood flow to the fingers and toes, causing them to feel cold and numb.
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick, making it harder for the heart to pump blood.
Benefits of Amlodipine
1. Effective Blood Pressure Control
Amlodipine is highly effective in lowering blood pressure, making it a valuable tool in the management of hypertension. By reducing blood pressure, Amlodipine helps to decrease the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
2. Reduction in Angina Symptoms
For patients with chronic stable angina or vasospastic angina, Amlodipine can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of chest pain episodes. This improvement in symptoms can lead to a better quality of life and increased physical activity.
3. Long-Lasting Effect
One of the key benefits of Amlodipine is its long duration of action. It is typically taken once daily, which makes it convenient for patients to adhere to their treatment regimen. The long-lasting effect also helps to maintain consistent blood pressure control throughout the day.
4. Well-Tolerated
Amlodipine is generally well-tolerated by most patients. It has a favorable safety profile, and serious side effects are rare. This makes it a suitable option for a wide range of patients, including the elderly and those with other medical conditions.
5. Combination Therapy
Amlodipine can be used in combination with other antihypertensive medications, such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, or diuretics, to achieve optimal blood pressure control. This flexibility allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to the individual needs of each patient.
Side Effects of Amlodipine
While Amlodipine is generally well-tolerated, like all medications, it can cause side effects. The most common side effects are usually mild and may include:
1. Common Side Effects
- Swelling (Edema): One of the most common side effects of Amlodipine is swelling in the ankles, feet, or hands. This occurs due to the relaxation of blood vessels, which can cause fluid to accumulate in the tissues.
- Dizziness: Some patients may experience dizziness, especially when standing up quickly. This is usually mild and tends to improve over time.
- Flushing: Amlodipine can cause a feeling of warmth or redness in the face, known as flushing. This is generally harmless and temporary.
- Headache: Headaches are a common side effect of Amlodipine, but they are usually mild and resolve on their own.
- Fatigue: Some patients may feel tired or fatigued while taking Amlodipine. This is typically mild and improves with continued use.
2. Less Common Side Effects
- Palpitations: Some patients may experience a sensation of a racing or irregular heartbeat. This is usually not serious but should be reported to a healthcare provider if it persists.
- Nausea: Nausea is a less common side effect of Amlodipine, but it can occur in some patients.
- Abdominal Pain: Some patients may experience mild abdominal pain or discomfort while taking Amlodipine.
- Muscle Cramps: In rare cases, Amlodipine may cause muscle cramps or stiffness.
3. Serious Side Effects
While serious side effects are rare, they can occur. Patients should seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of the following:
- Severe Dizziness or Fainting: This could indicate a significant drop in blood pressure and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath could be a sign of a serious allergic reaction or heart problem.
- Chest Pain: While Amlodipine is used to treat angina, new or worsening chest pain should be evaluated immediately.
- Swelling of the Face, Lips, or Tongue: This could indicate an allergic reaction and requires immediate medical attention.
- Irregular Heartbeat: A rapid or irregular heartbeat that persists should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Dosage and Administration
1. Recommended Dosage
The dosage of Amlodipine varies depending on the condition being treated and the patient’s individual response to the medication. The typical starting dose for most adults is 5 mg once daily. The dose may be increased to a maximum of 10 mg once daily if necessary.
For elderly patients or those with liver impairment, a lower starting dose of 2.5 mg once daily may be recommended.
2. How to Take Amlodipine
- Timing: Amlodipine is usually taken once daily, with or without food. It is important to take it at the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels of the medication.
- Missed Dose: If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, the missed dose should be skipped, and the regular dosing schedule should be resumed. Double doses should not be taken to make up for a missed dose.
- Overdose: In case of an overdose, medical attention should be sought immediately. Symptoms of overdose may include severe dizziness, fainting, or a rapid heartbeat.
3. Special Populations
- Elderly: Elderly patients may be more sensitive to the effects of Amlodipine and may require a lower starting dose.
- Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of Amlodipine in children have not been established.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Amlodipine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. It is not known whether Amlodipine is excreted in breast milk, so caution should be exercised when prescribing it to breastfeeding women.

Warnings and Precautions
1. Hypotension (Low Blood Pressure)
Amlodipine can cause a significant drop in blood pressure, especially in patients who are already taking other antihypertensive medications. Patients should be monitored for signs of hypotension, such as dizziness or fainting, especially when starting Amlodipine or increasing the dose.
2. Liver Impairment
Amlodipine is metabolized in the liver, so patients with liver impairment may require a lower dose. Liver function should be monitored regularly in these patients.
3. Heart Failure
In patients with heart failure, Amlodipine should be used with caution. While it is generally safe, it may worsen symptoms in some patients, particularly those with severe heart failure.
4. Peripheral Edema
Amlodipine can cause swelling in the extremities, particularly the ankles and feet. This side effect is more common in elderly patients and those taking higher doses. If swelling becomes severe or bothersome, the dose may need to be adjusted.
5. Drug Interactions
Amlodipine can interact with other medications, potentially affecting its efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Some common drug interactions include:
- Other Antihypertensive Medications: Combining Amlodipine with other blood pressure-lowering drugs can increase the risk of hypotension.
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Medications that inhibit the CYP3A4 enzyme, such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and ritonavir, can increase the levels of Amlodipine in the blood, potentially leading to an increased risk of side effects.
- Grapefruit Juice: Grapefruit juice can inhibit the metabolism of Amlodipine, leading to increased blood levels of the medication. Patients should avoid consuming grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking Amlodipine.
6. Allergic Reactions
Patients who are allergic to Amlodipine or other calcium channel blockers should not take this medication. Signs of an allergic reaction include rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, and difficulty breathing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can Amlodipine be taken with other medications?
Yes, Amlodipine can be taken with other medications, but it is important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Some medications may interact with Amlodipine, affecting its efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects.
2. How long does it take for Amlodipine to work?
Amlodipine starts to work within a few hours of taking the first dose, but it may take several weeks to see the full effects on blood pressure. It is important to continue taking the medication as prescribed, even if you do not notice immediate improvements.
3. Can Amlodipine be stopped abruptly?
Amlodipine should not be stopped abruptly without consulting your healthcare provider. Suddenly stopping the medication can cause a rebound increase in blood pressure, which can be dangerous. If you need to stop taking Amlodipine, your healthcare provider will advise you on how to do so safely.
4. Is Amlodipine safe for long-term use?
Amlodipine is generally safe for long-term use when taken as prescribed. It is important to have regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your blood pressure and overall health while taking Amlodipine.
5. Can Amlodipine cause weight gain?
Weight gain is not a common side effect of Amlodipine. However, some patients may experience fluid retention, which can lead to swelling in the ankles and feet. If you notice significant weight gain or swelling, you should consult your healthcare provider.
6. Can Amlodipine be taken during pregnancy?
Amlodipine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, you should discuss the risks and benefits of taking Amlodipine with your healthcare provider.
7. Can Amlodipine be taken with alcohol?
Moderate alcohol consumption is generally safe while taking Amlodipine. However, excessive alcohol intake can increase the risk of side effects, such as dizziness and low blood pressure. It is important to drink alcohol in moderation and consult your healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
8. What are the benefits of Amlodipine?
- Effectively lowers blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes
- Helps manage angina by improving blood flow to the heart
- Can be used alone or with other medications for better control of hypertension
9. What are the common side effects of Amlodipine?
- Swelling in the legs or ankles (edema)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Flushing (warmth or redness in the face)
- Fatigue
- Nausea
10. Are there any serious side effects of Amlodipine?
Serious side effects are rare but may include:
- Severe dizziness or fainting
- Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- Shortness of breath
- Severe swelling of the hands, face, or tongue (allergic reaction)
11. What is the recommended dosage for Amlodipine?
- Hypertension & Angina: 5 mg once daily (may be increased to 10 mg daily if needed)
- Children (6-17 years): 2.5–5 mg once daily
Dosage should be determined by a doctor based on individual needs.
Conclusion
Amlodipine is a widely used and effective medication for the treatment of hypertension and angina. Its long-lasting effect, favorable safety profile, and ease of use make it a popular choice among healthcare providers and patients alike. While Amlodipine is generally well-tolerated, it is important to be aware of potential side effects and drug interactions. Patients should always follow their healthcare provider’s instructions and report any unusual symptoms or concerns.
If you have been prescribed Amlodipine, it is important to take it as directed and attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor your blood pressure and overall health. By working closely with your healthcare provider, you can achieve optimal blood pressure control and reduce your risk of cardiovascular complications.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medication.

